Sauces
Sauce (from French sauce - gravy) - a liquid seasoning for the main dish. Sauces are not only served with ready-made dishes, but are also used in the process of their preparation (that is, they cut products in sauce or bake under sauce). Sauces have been known since antiquity (for example, the ancient Roman garum, also known as liquamen, is made from small fermented fish, an analogue of Thai nam pla and Vietnamese nyok nam).
Each sauce consists of a liquid base and additional ingredients - vegetables, fruits, herbs, spices, spices. There are not many basic, basic sauces prepared on a certain liquid basis. A great variety of other sauces are all sorts of variations on the main ones.
Approximate classification of sauces
A. Sauces with flour on broths - meat, fish, mushroom. These include the main sauces Espagnol and Veloute. Espagnol is the main brown sauce, made from red roux (that is, fried in butter until golden brown wheat flour) and strong meat broth (fume). Derivatives include demi-voice, ju-lier, perigueux, robert. Velute is the main white sauce, made from golden (that is, not fried so much) ru and light chicken, veal or fish fume. Derivatives include allemand, privateer, pullet, as well as Georgian national satsivi, etc.
B. Sauces with flour on vegetable and cereal broths
B. Sauces with flour on milk and fermented milk products. This type includes the classic béchamel, a basic milk sauce that is made with white rue (wheat fried in butter without discoloration) and milk.
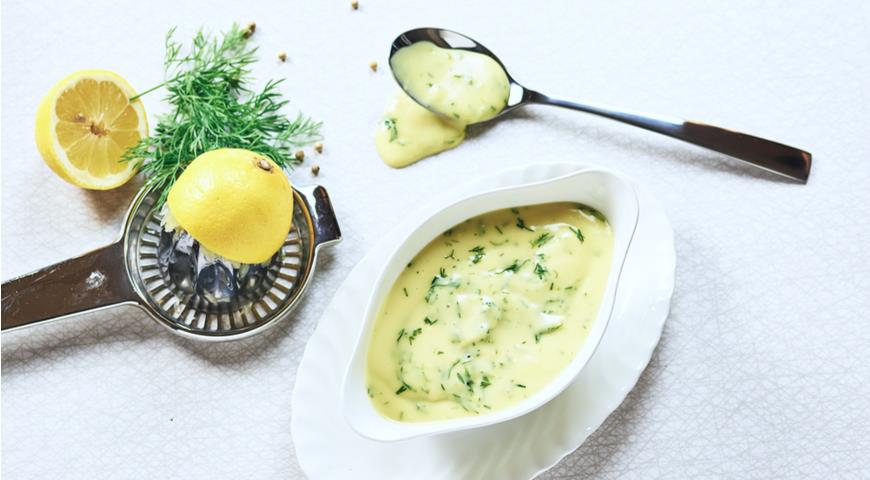
D. Sauces with butter. One of the main sauces in French culinary theory is the so-called. Dutch, i.e. an emulsion prepared in a water bath from egg yolk and butter. Derivatives - shoron, menier, béarna, dijon sauces.
E. Sauces with vegetable oil. The most important of them is mayonnaise, among others - aioli, tartar, remoulade. Pesto is also made in oil.
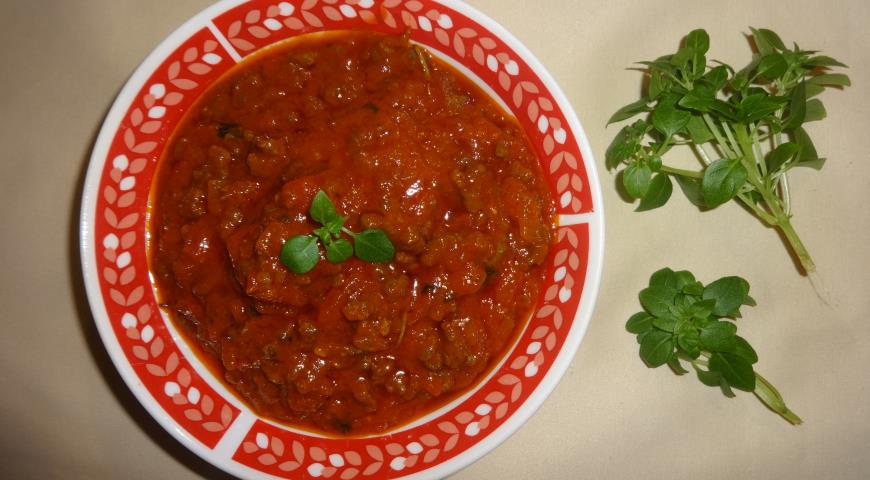
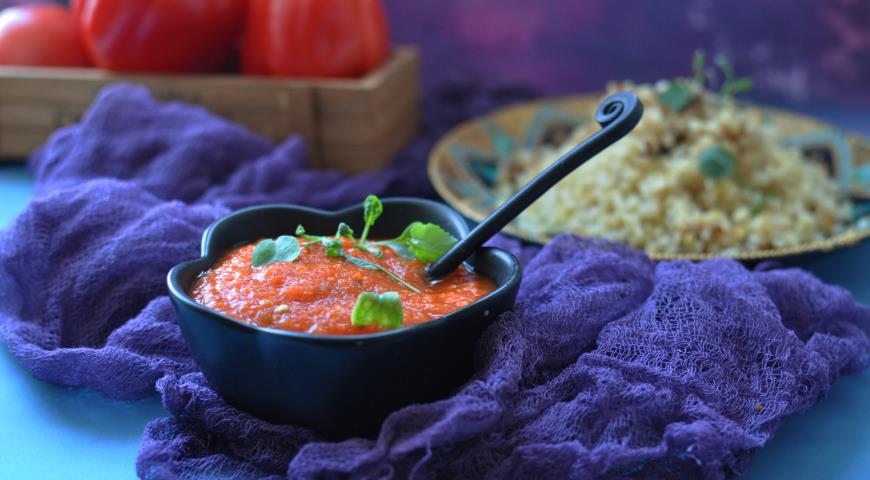
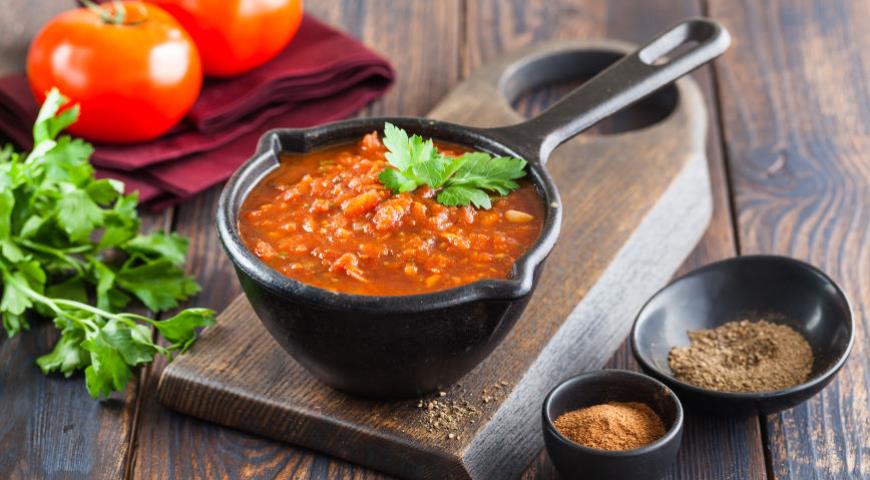
E. Sauces from grated, chopped or boiled vegetables, fruits, berries. This type includes tomato sauces, tkemali, various chutneys, bolognese (with minced meat), sauces based on hot peppers (tabasco, harissa, etc.), mostarda, gauacamole.
G. Sauces based on juices and vinegar. This type includes, for example, pomegranate sauces (narsharab), cumberland.
H. Sauces based on fermented products, including fish (Thai nam pla, Vietnamese nyok nam), soy sauces (hoisin, teriyaki).
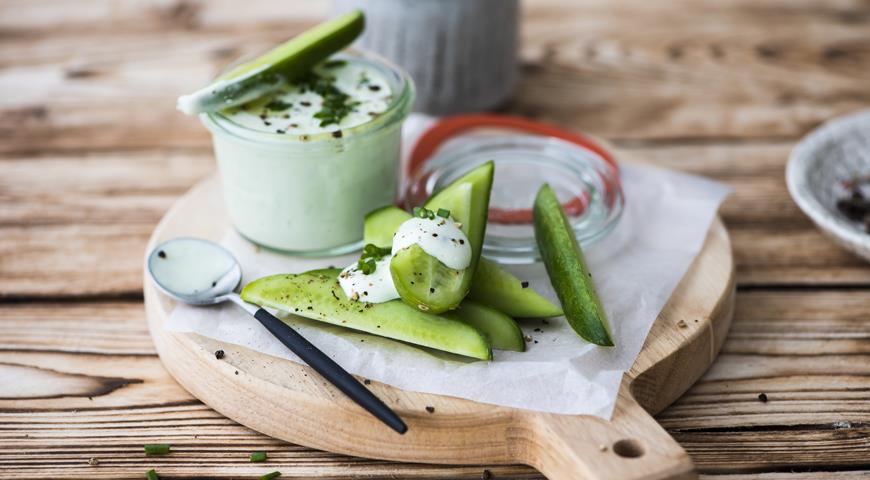
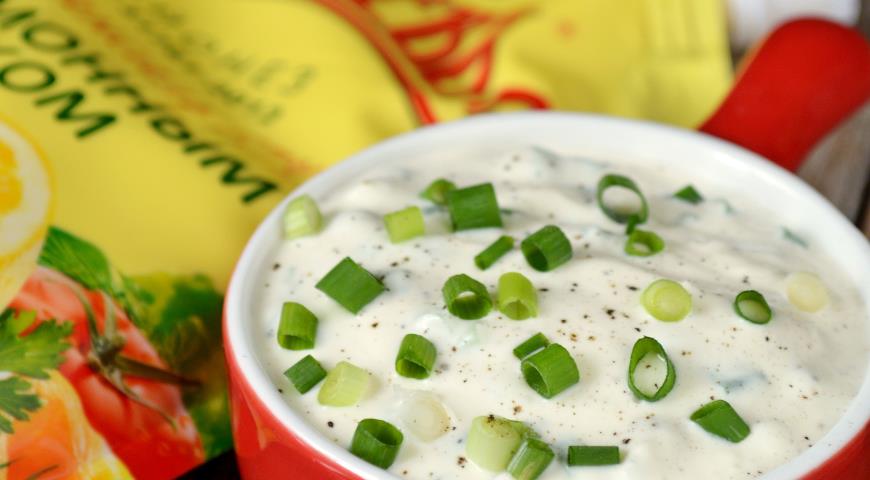
I. Sauces based on thick fermented milk products - sour cream, yogurt, etc. dzaziki belongs to them.
K. Sweet sauces, which are prepared from a variety of fruit and berry decoctions, juices, milk, red wine. Sugar, vanillin, chocolate, cocoa serve as an additional part. These sauces use potato starch as a thickener, and some use flour.
According to the consistency, all sauces can be divided into liquid sauces and thick dips (English dip), intended for dipping chips, pieces of vegetables, fruits, meat, seafood in it. That is, the main course is not poured over the sauce, but the food is dipped in the sauce. Dip can be considered mayonnaise, guacamole, hummus, sour cream, dzaziki, fondue, etc.